Obstructive Jaundice
Obstructive Jaundice – Condition Overview
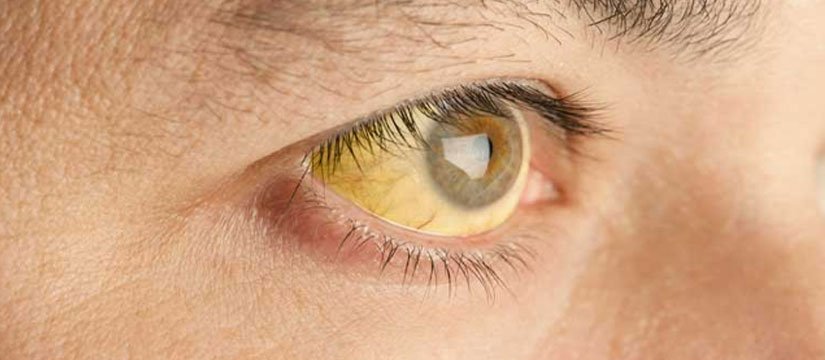
Obstructive jaundice occurs when the flow of bile from the liver to the small intestine is blocked. This leads to a buildup of bilirubin in the blood, causing yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Common causes include bile duct stones, strictures, tumors, or inflammation. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent serious liver damage or infections.
Symptoms of Obstructive Jaundice
- Yellowing of eyes and skin
- Dark urine and pale stools
- Itching (pruritus)
- Upper right abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever and chills if infection (cholangitis) occurs
Causes of Obstructive Jaundice
- Bile duct stones (choledocholithiasis)
- Strictures or narrowing of the bile ducts
- Tumors in the bile duct, pancreas, or liver
- Inflammation or infection of the bile ducts (cholangitis)
- Post-surgical complications affecting bile flow
Treatment of Obstructive Jaundice
- Endoscopic procedures (ERCP) to remove stones or place stents
- Surgery to remove tumors or correct strictures
- Medications to treat infections and reduce itching
- Supportive care including hydration and nutrition
Early detection and timely treatment prevent complications like liver failure and severe infections. For expert care, Contact us.


